


Next: Structural Equations
Up: Reaction Time Mean and
Previous: Results
In the literature, a wide variety of probability distributions are
proposed to account for RT data. Among these, the gamma distribution
was the favorite (see e.g., Bush & Mosteller, 1955;
Christie, 1952; Luce, 1960; Restle, 1961). The gamma distribution can
be considered as a special case of the Poisson-Erlang distribution,
arising if the number of distractions is assumed to be constant. In that
particular case the gamma distribution is referred to as the Erlang
distribution. The Erlang distribution has three parameters: the parameter
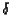 ,
which again represents the transition rate to switch from
distraction to work, the number of distraction N and real total
working time A. Note, that N is assumed to be constant across
RTs. According to the Erlang model, expectation and variance can be
written as
,
which again represents the transition rate to switch from
distraction to work, the number of distraction N and real total
working time A. Note, that N is assumed to be constant across
RTs. According to the Erlang model, expectation and variance can be
written as
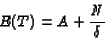 |
(10) |
and
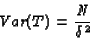 |
(11) |
Taking the natural logarithm of both sides one obtains:
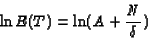 |
(12) |
and
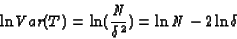 |
(13) |
As was the case in the Poisson-Erlang model, in the Erlang model
the logarithm of the variance is also a linear function of the logarithm
of the parameters, that is the parameters N and 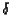 .
And also
similar to the Poisson-Erlang model, in the Erlang model
this is not the case with respect to the logarithm of the expectation.
But, again, in the Erlang model the difference between
the expectation E(T) and the real total working time A:
E(T)-A is
a linear function of the logarithm of the Erlang parameters:
.
And also
similar to the Poisson-Erlang model, in the Erlang model
this is not the case with respect to the logarithm of the expectation.
But, again, in the Erlang model the difference between
the expectation E(T) and the real total working time A:
E(T)-A is
a linear function of the logarithm of the Erlang parameters:
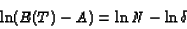 |
(14) |
So, according to the simpler Erlang model,
the correlation across subjects between
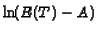 and
and
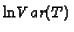 is also linearly dependent on
the log parameters
is also linearly dependent on
the log parameters 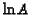 ,
,
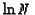 and
and
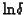 .
.



Next: Structural Equations
Up: Reaction Time Mean and
Previous: Results
AHGS VAN DER VEN
2002-01-14